
Dementia Screening Singapore – MRI Brain Imaging For Dementia Assessment
Understanding Dementia
Dementia is a condition that causes progressive intellectual decline, leading to increasing difficulties in coping with everyday activities. It’s essential to recognise that dementia is not a normal part of ageing.
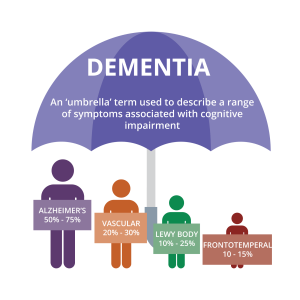
Types of Dementia
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common type of dementia. The second most common type of dementia is Vascular Dementia.
What are the early signs of Dementia?
Recognising early signs is crucial for timely intervention. Here are common indicators:
- Memory Loss:
- Disrupts daily life.
- Difficulty recalling recent events or names.
- Problem-Solving Challenges:
- Struggles with planning and solving tasks.
- Difficulty Completing Familiar Tasks:
- At home, work, or during leisure activities.
- Confusion with Time or Place:
- Losing track of dates, seasons, or locations.
- Visual and Spatial Difficulties:
- Trouble understanding images and spatial relationships.
- Language Problems:
- New issues with speaking or writing.
- Misplacing Items:
- Losing items and inability to retrace steps.
- Judgment Impairment:
- Decreased ability to make sound decisions.
- Social Withdrawal:
- Reduced participation in work or social activities.
- Mood and Personality Changes:
- Shifts in behaviour, emotions, or personality.
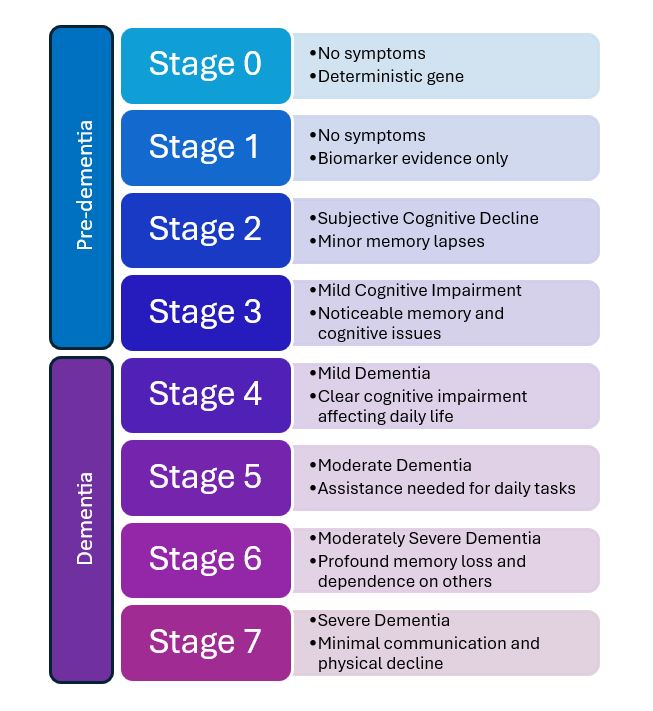
What are the stages of Dementia?
Combining the Reisberg Scale(1) (Global Deterioration Scale) with the NIA-AA(2) (National Institute of Aging and the Alzheimer’s Association) staging of Alzheimer’s disease, dementia can be categorised as follows:
Dementia in Asia
Approximately 1 in 10 individuals aged 60 and above in Singapore are affected by dementia, as reported by a 2015 study conducted by the Institute of Mental Health(3).
Presently, around 80,000 people in Singapore are living with dementia. This number is projected to rise to 100,000 by the year 2030(4).
The ongoing Biomarker and Cognitive Impairment Study (BioCIS) by the Dementia Research Centre (Singapore) (DRCS) has yielded significant preliminary insights(5):
- Asian patients are three times more likely than Caucasians to experience silent strokes due to narrowing of small blood vessels in the brain. In brain scans, these silent strokes manifest as lesions or ‘white matter hyperintensity’. Such lesions serve as early indicators of an increased risk of dementia.
- Additionally, the APOE4 gene, a known genetic biomarker for dementia risk, is less prevalent in Asians compared to Caucasians. However, individuals without the APOE4 gene may experience greater brain shrinkage due to small vessel disease. Consequently, Asians face a higher risk of brain shrinkage associated with this condition.
- The BioCIS study underscores that many people remain undetected for cognitive impairment.
Forgetfulness vs Dementia
It’s common to experience occasional forgetfulness, especially as we age. However, if you notice significant changes in memory or cognitive function, it’s essential to seek professional advice. They can assess whether it’s age-related forgetfulness, pre-dementia, or potentially dementia.
Early detection and Dementia
Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia are the two most common causes of dementia. Their early detection has benefits to both physicians and patients. Through early detection, patients gain insight into their condition and its progression. Physicians are also able to educate patients on the available treatment options.
While there’s no single definitive test for early detection of Alzheimer’s disease, MRI brain imaging plays a crucial role. NeuroQuant®(6), an FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) and HSA (Singapore Health Science Authority) approved tool, aids in post-processing MRI data. It provides valuable information about brain structures, volumes, and potential abnormalities.
Of note, young onset dementia affects individuals below 65 years old. Notably, patients as young as 45 years have been diagnosed in Singapore.
NeuroQuant®: Enhancing MRI Brain Imaging for Dementia Assessment(6)
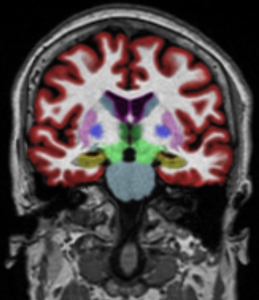
NeuroQuant® is an advanced AI tool that analyses high-resolution brain images. It is like a digital ruler placed over the brain to precisely measure the volume of critical brain structures, including the hippocampus, which is associated with memory and learning; the entorhinal cortex, which is vital for memory consolidation; and the temporal lobes, which are essential for various cognitive functions. Shrinkage of these structures serve as non-specific biomarkers of underlying Alzheimer’s disease pathology.
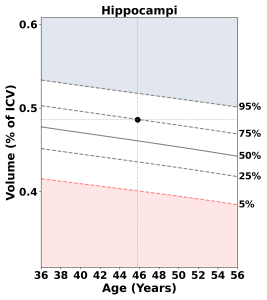
NeuroQuant® generates concise reports detailing brain structure volumes. These values are also compared to age-appropriate reference distributions. Clinicians then use these reports to evaluate patients showing early signs of Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia.
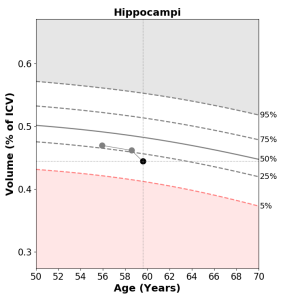
NeuroQuant® may also be used for comparative purposes. The causes of dementia are generally progressive neurodegenerative diseases. Thus, physicians may first get a “baseline” study of a patient’s brain, and then have follow up exams at prescribed intervals to reveal brain atrophy and its rate over time.
In addition, the standard MRI brain evaluation performed with NeuroQuant® assists the clinician in determining other potential causes of dementia, such as vascular dementia, fronto-temporal dementia (FTLD), and posterior cortical atrophy (PCA). The standard MRI brain also assists the clinician in evaluating possible tumours, strokes, and microbleeds.
Understanding Positive Biomarkers and Dementia
Diagnosing dementia is complex, and there’s no single definitive test. Biomarkers play a crucial role, but they are non-specific on their own. On MRI scans, specific brain changes serve as indicators but don’t pinpoint a particular diagnosis.
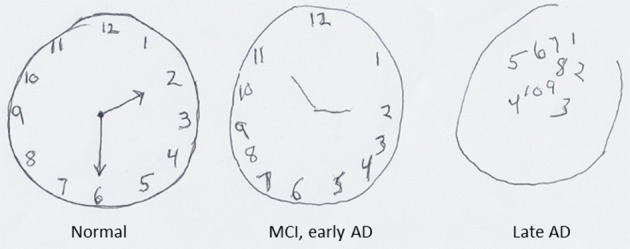
Source: Montreal Cognitive Assessment. (2024, February 14). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Montreal_Cognitive_Assessment
Your physician correlates these MRI findings with clinical history about your symptoms, medical background, and cognitive decline. They will also correlate with cognitive testing, including the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) or the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MOCA).
Based on these various components and the MRI brain findings, your physician may recommend a follow up MRI with Neuroquant® if needed, or proceed to test for Amyloid and Tau proteins, which are core biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease pathology. In some instances, no further tests may be required for diagnosis or treatment.
Advancements in Dementia Treatment
Significant progress in recent years has led to the development of two drugs that show promise in halting the progression of dementia, mainly targeting Alzheimer’s disease. Aducanumab was approved in 2022 by the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration), and Lecanemab in 2023. Both these drugs have shown efficacy in clinical trials that were carried out in Singapore.
Reducing the Risk of Dementia
Brain changes can begin decades before dementia symptoms appear, so taking early preventive measures is essential. While we can’t reverse the underlying mechanisms of Alzheimer’s disease, we can certainly address risk factors like hypertension and cardiovascular health. By making these lifestyle adjustments, you’re not only reducing your risk of dementia but also promoting overall well-being.
Here are some practical steps you can take:
- Stay Physically Active:
- Regular exercise is one of the best ways to reduce your risk of dementia. It helps improve blood flow to the brain and supports overall cardiovascular health.
- Adopt a Brain-Healthy Diet:
- A Mediterranean diet which is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Foods high in antioxidants (such as berries) and omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish) are particularly beneficial for brain health.
- Avoid Smoking:
- Smoking is harmful to both your cardiovascular system and your brain. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce your risk of developing dementia.
- Control Blood Pressure:
- High blood pressure is a major risk factor for vascular dementia. Regular monitoring and management of blood pressure are essential. Reducing salt intake and staying physically active are lifestyle changes that can help.
- Exercise Your Mind:
- Read, solve puzzles, learn new skills, play musical instruments, or engage in activities that challenge your cognitive abilities. Mental stimulation helps maintain brain health.
MRI Brain Imaging with NeuroQuant® is available at Asiamedic
Reach out to your physician or healthcare provider to inform them about your interest in MRI Brain Imaging with NeuroQuant®.
Asiamedic offers two options for MRI Brain Imaging with NeuroQuant®:
- MRI Dementia Complete*: Includes MRI Brain + MR Angiography Brain + NeuroQuant®
- MRI Dementia Plus*: Includes MRI Brain + NeuroQuant®
Discuss your specific needs and symptoms with your physician. They will guide you on the most suitable option for you.
MRI Brain imaging with NeuroQuant® is a highly valuable study that aids clinicians in the diagnosis, treatment, and surveillance of dementia.
* No IV contrast is required for routine scans
References:
- Reisberg B, et al. The Global Deterioration Scale for assessment of primary degenerative dementia. Am J Psychiatry. 1982 Sep;139(9):1136-9. doi: 10.1176/ajp.139.9.1136. PMID: 7114305.
- Alzheimer’s Association. Revised Criteria for Diagnosis and Staging of Alzheimer’s Disease: Alzheimer’s Association Workgroup. https://aaic.alz.org/diagnostic-criteria.asp
- Subramaniam M, Chong SA, et al. Prevalence of Dementia in People Aged 60 Years and Above: Results from the WiSE Study. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;45(4):1127-38. doi: 10.3233/JAD-142769. PMID: 25672767.
- The Straits Times (Singapore). (2023, 25-July). Doctors can bring in new US-approved drug for early-stage Alzheimer’s disease. https://www.straitstimes.com/singapore/new-us-approved-drug-for-early-stage-alzheimer-s-disease-not-yet-available-here
- The Straits Times (Singapore). (2023, June 21). Asian dementia on the rise in Singapore. https://www.straitstimes.com/life/home-design/asian-dementia-on-the-rise-in-singapore
- Cortechs.ai. NeuroQuant®. https://www.cortechs.ai/solution/neuroquant/



